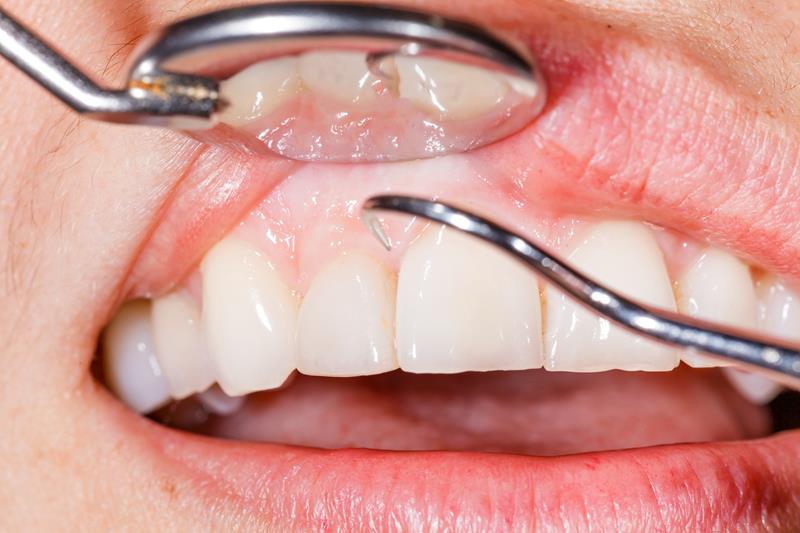
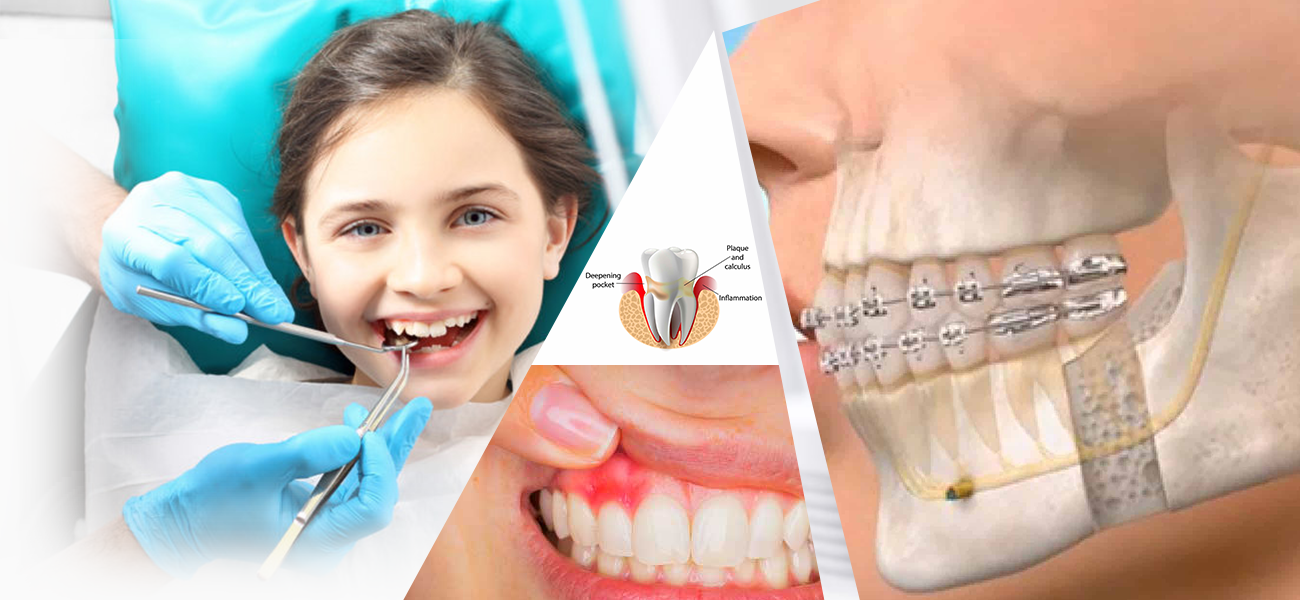
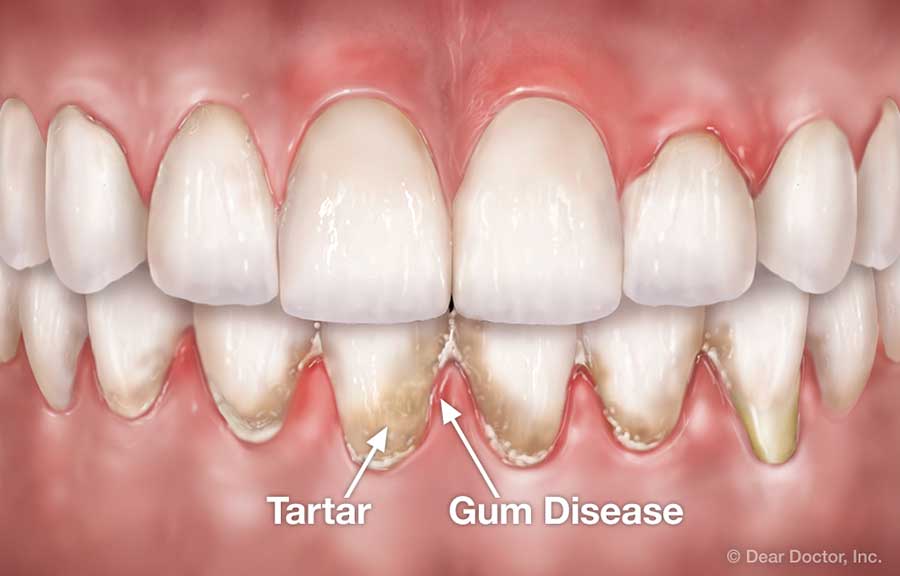
Gum disease refers to inflammation of the soft tissue (gingiva) and abnormal loss of bone that surrounds the teeth and holds them in place. Gum disease is the second most common cause of toothache. Treatment of early gum disease involves oral hygiene and removal of bacterial plaque. Moderate to advanced gum disease usually requires a thorough cleaning of the teeth and teeth roots called “root planing†and “subgingival curettage.†Root planing is the removal of plaque and tartar (hardened plaque) from exposed teeth roots while subgingival curettage refers to the removal of the surface of the inflamed layer of gum tissue. Both of these procedures are usually performed under local anesthesia and may be accompanied by the use of oral antibiotics to overcome gum infection or abscess. Follow-up gum treatment may include various types of gum surgeries. In advanced gum disease with significant bone destruction and loosening of teeth, teeth splinting or teeth extractions may be necessary.